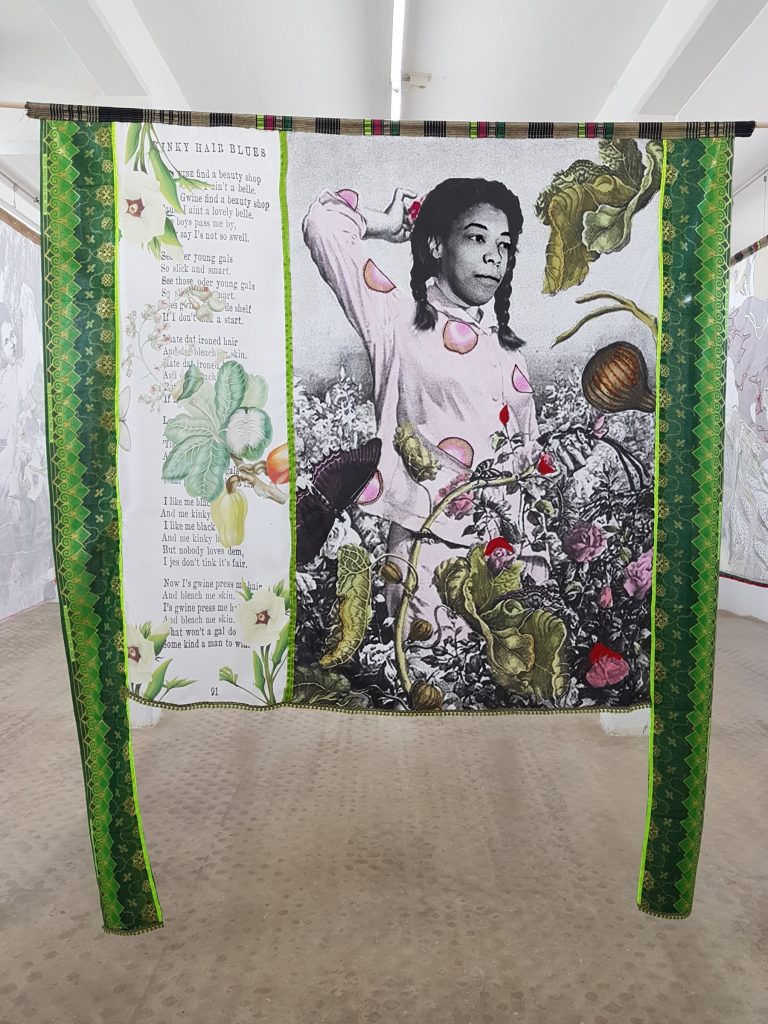
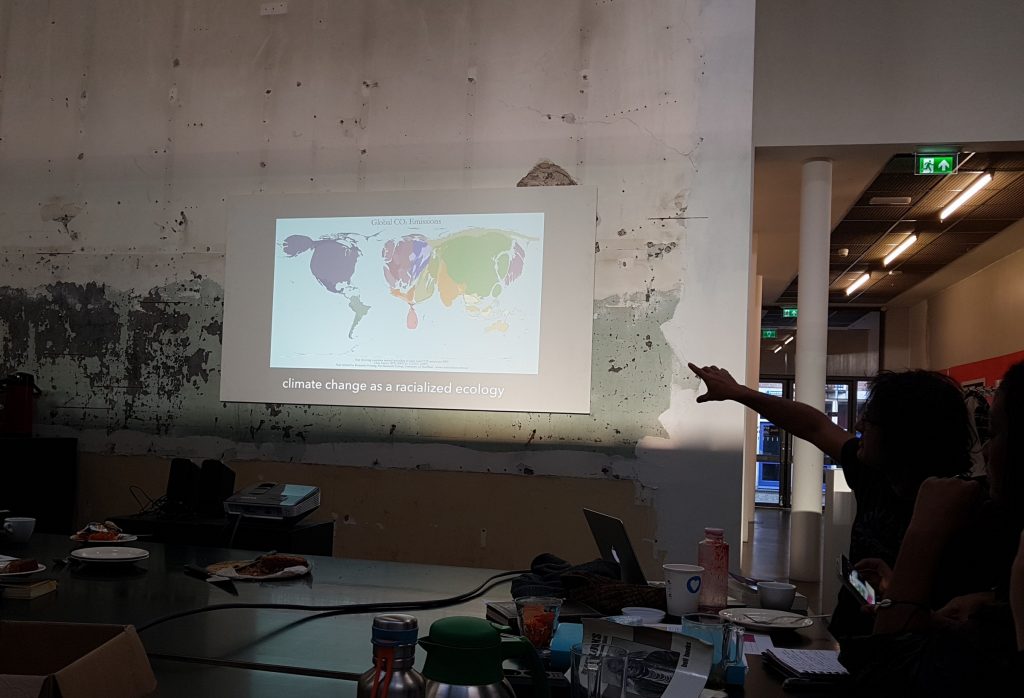
Evolutionary Populations: Seeds of a World Waiting to Germinate
With the outbreak of civil war in Syria in 2011, agronomist and phyto-geneticist, Salvatore Ceccarelli was forced to end his 25-year research period in Syria where he had been working with local farmers experimenting with a revolutionary agricultural method that develops participatory plant breeding, a type of breeding done in collaboration with farmers to breed diverse seed lines (in particular barley and durum wheat) which enable greater biodiversity and crop adaptation to the environment. As a farming method this participatory plant breeding is able to respond ethically to contemporary agroecological challenges: ensuring food security despite climate-related uncertainties and safeguarding diversity to improve the nutritional characteristics of the crops and giving control of the seeds back to the farmers thus creating strong participatory and commoning dynamics. So as not to risk losing the years of participatory seed cultivation by Syrian farmers, Ceccarelli managed to bring a small quantity of many hundreds of seed varieties to Italy. These seeds were planted in different parts of Italy and within a few years the practice of participatory genetic evolution started to take ground, a practice which challenges the cultural certainties tied to concepts such as monoculture, uniformity, and genetic selection.
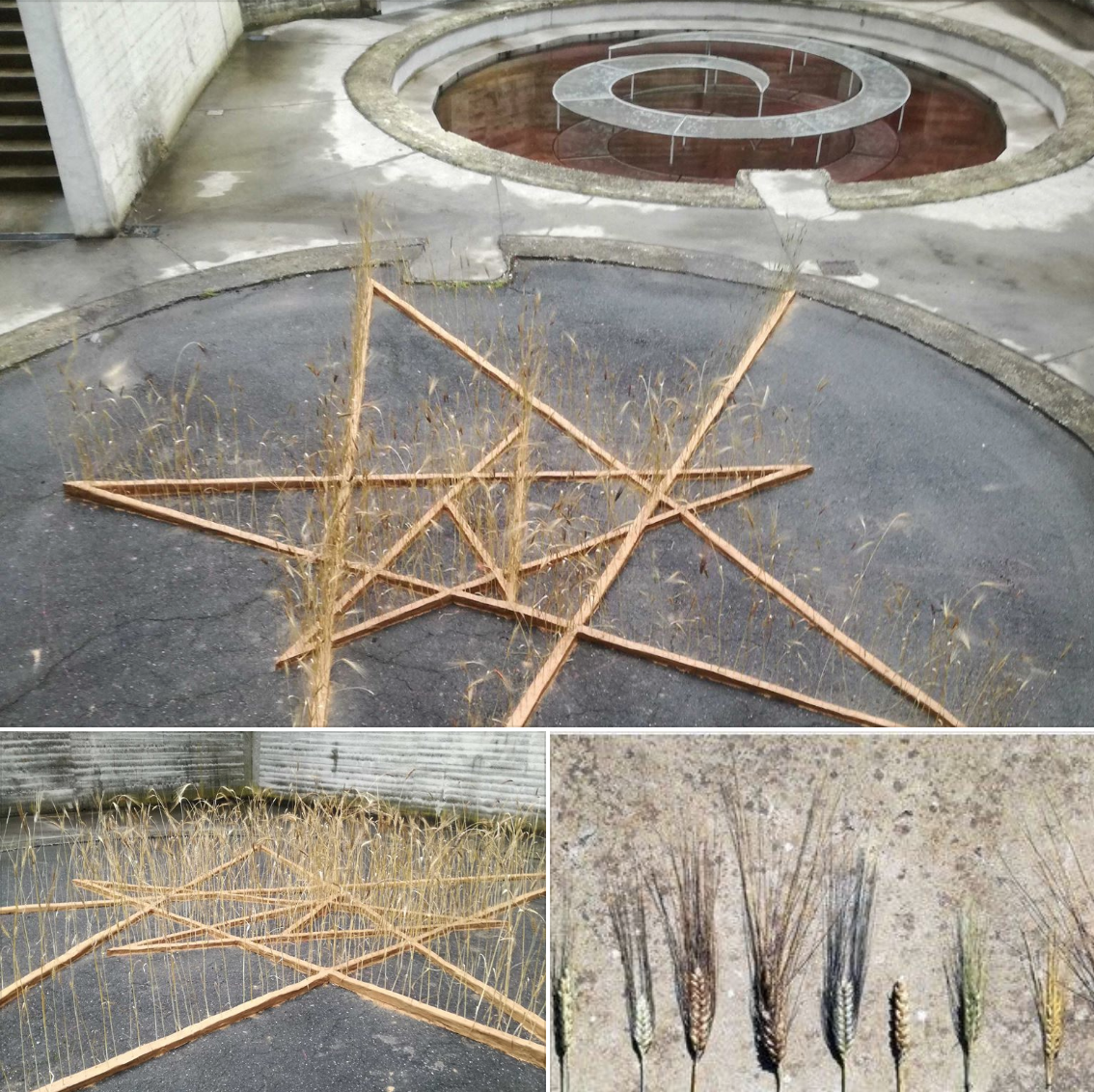
As part of the Meteorite in Giardino II (Meteorite in the Garden) program at Fondazione Merz in Turin 07.06–10.07.2018, Luigi Coppola has created an installation which reassembles—according to a design symbolically referring to the complexity of nature—hundreds of grain-bearing ears of barley and wheat which have been planted from seeds cultivated through participatory seed evolution in Salento, Italy together with the Casa delle Agriculture (House of Agricultures), with which Coppola has been working for the past five years on regenerative agricultural practices alongside social, political, and cultural activation of the community.